Youtube Comments Sentiment Analysis
Source
Introduction
Sentiment analysis helps interpret user opinions and emotions from text, making it essential for understanding audience feedback. In this project, I will use some deep learning models (MLP, CNN, LSTM) trained on IMDB data to inference sentiment in Amazon reviews. Building on this, we develop a simple Streamlit app to analyze and predict the sentiment of YouTube comments in real-time, combining practical NLP techniques with an interactive user interface.

In this project, we will implement 3 main steps:
- Data preparation (EDA, Cleaning, Word Embedding with Glove)
- Model training using Simple Neutral Net (or MLP), Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) and Convoluational Neutral Network (CNN) with 1D for 1 dimension data embbeded
- Inference on Amazon reviews dataset and build a simple Streamlit app with Youtube API to analyze Youtube comments
Data preparation
About Dataset
In this project, we used the IMDB dataset which is a Large Movie Review Dataset from Hugging Face for training models. This is a dataset for binary sentiment classification containing substantially more data than previous benchmark datasets. We provide a set of 25,000 highly polar movie reviews for training, and 25,000 for testing. There is additional unlabeled data for use as well.
Dataset structure:
text: astringfeature.label: a classification label, with possible values includingneg(0),pos(1).
Data Cleaning
In this step, OG will implement some data cleaning with text using nltk module. This is a powerful module for text transformation and really suitable for us to use in this step. We will ultilize nltk combine with regex to do these tasks:
- Lower text: Lower all text
- Remove html tags: There are potentially some html tags in the raw text, this task will replace it with space
- Change the abbreviated into full word: Adjust the abbreviated word like
didn'tto full worddid not - Remove punctuations and numbers: punctuation and number might doesn’t have too many meaning, to standardize our text, we will remove it
- Replace multi space with 1 space
- Remove stopwords (except the
notword because we still need it to represent the negative sentiment)
def cleaning_text(text):
'''clean up text'''
text = text.lower()
#remove html tags
Tag_re = re.compile(r'<[^>]+>')
text = Tag_re.sub(' ', text)
#change abbreviated into full words
text = remove_abb(text)
#remove punctuations and numbers
text = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z]', ' ', text)
#Single character removal
text = re.sub(r'\s+[a-zA-Z]\s+', ' ', text)
#remove multiple spaces
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text)
#remove stopwords
stopwords_list = [word for word in stopwords.words('english') if word != 'not']
pattern = re.compile(r'\b(' + r'|'.join(stopwords_list) + r')\b\s*')
text = pattern.sub('', text)
return textAfter cleaning, we split data into train and test:
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(reviews, np.array(raw_data['label']), test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
print("X_train:", len(X_train)) # X_train: 40000
print("X_test:", len(X_test)) # X_test: 10000
print("y_train:", len(y_train)) # y_train: 40000
print("y_test:", len(y_test)) # y_test: 10000GloVe Embedding
In this project, we’ll use GloVe (Global Vectors) which is an open-source of Standford aims to create the vectors represent for words using GloVe vector space model. GloVe page provide 4 files contain vectors trained on many huge web dataset (Wikipedia 2014 + Gigaword 5). We will use the file glove.6B.100d.txt from Kaggle glove.6B.100d which contain about 400K diferrent words in 100 dimension vector space.
Firstly before apply the Glove, we have to tokenize out corpus to numeric and build our vocabulary dictionary.
# Using Tokenizer from keras.preprocessing.text
word_tokenizer = Tokenizer()
word_tokenizer.fit_on_texts(X_train) #train the tokenizer
# Convert to numeric form
X_train = word_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(X_train) # convert X_train to numeric form
X_test = word_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(X_test)To standardize our numeric vertor, we need to pad the reviews to the same length by adding 0 to the review which has length less than maxlen or eliminate the reviews which have length more than maxlen . We choose maxlen equals to 100 because we want it will fit with Glove word Embedding (which also have 100 dimensions for each word)
maxlen = 100
X_train = pad_sequences(X_train, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen)
X_test = pad_sequences(X_test, padding='post', maxlen=maxlen)Now, it’s time to build the word embedding matrix using Glove and map it to our vocabulary dictionary (the GloVe contain vector 100 dimension for each word). Map to our vocabulary dictionary, we suppose to have a matrix where each word corresponse to a vector from Glove.
# Read glove embedding file
embedd_dict = dict()
with open('glove.6B.100d.txt', 'r') as file:
for line in file:
values = line.split()
word = values[0]
coefs = np.asarray(values[1:], dtype='float32')
embedd_dict[word] = coefs
# Map the glove dict to our vocabulary matrix
embedding_matrix = np.zeros((vocab_size, 100))
for word, index in word_tokenizer.word_index.items():
embedding_vector = embedd_dict.get(word)
if embedding_vector is not None:
embedding_matrix[index] = embedding_vectorThe result size:

We ready for build our model with this embedding matrix
Models
Multi-Layers Perceptron (MLP)
We will buile a simple neutral network and add an embedding layer to it. This MLP model would have Flatten layer to flatten input data into 1D vevtor and Dense layer with 1 neuron and sigmoid activation (binary classification). This layer will return a result in range 0 and 1. If output close to 0, it indicates class 0 and class 1 consistently.
simple_nn_model = Sequential()
embedding_layer = Embedding(vocab_size, 100, weights=[embedding_matrix],input_length=maxlen, trainable=False)
#adding embedding layer into the model
simple_nn_model.add(embedding_layer)
#adding flatten and Dense layer
simple_nn_model.add(Flatten()) #flatten data into 1D vector
simple_nn_model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
simple_nn_model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])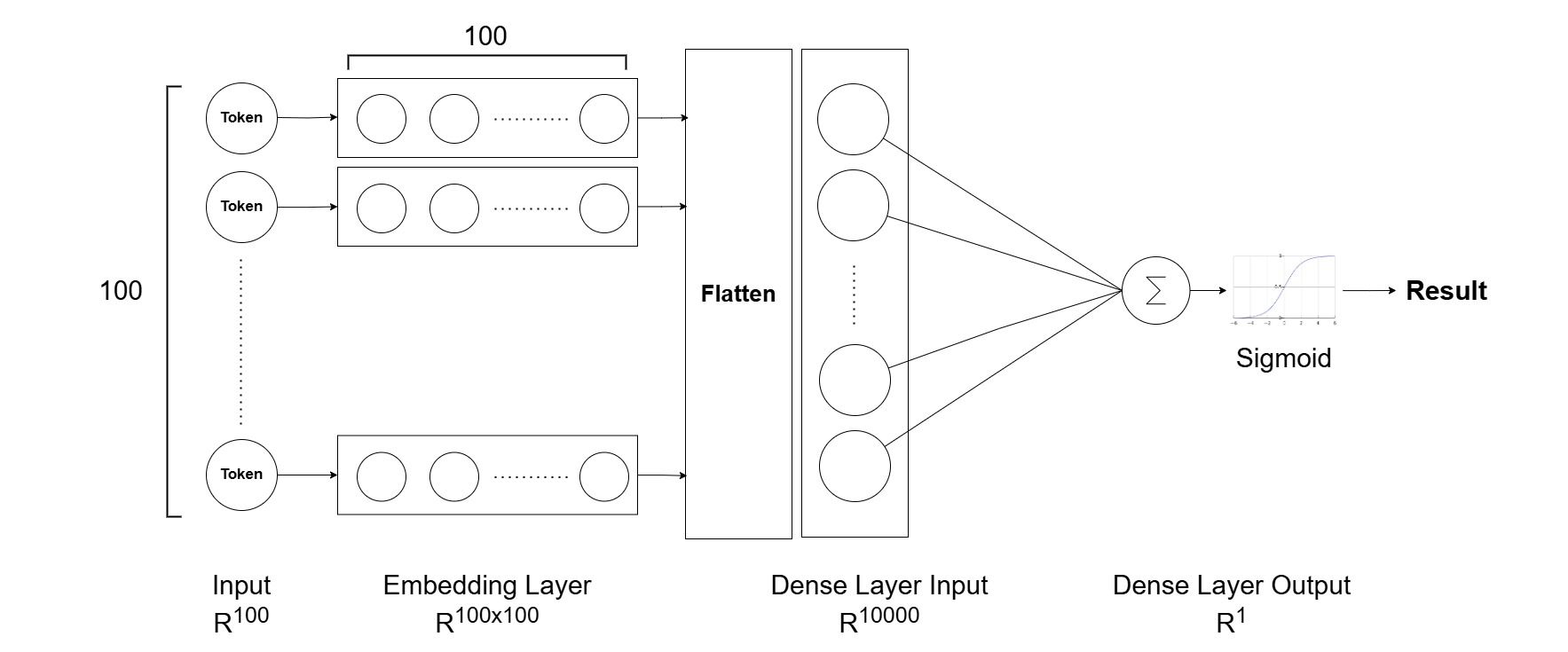
MLP architecture


In the Accuracy tab, it looks like our model is overfitting, it performed well on training set but not on test set. Accuracy is lower too much on test set than training set and loss is higher as well. Let move to CNN which more complex model to see how does it perform.
Convolutional Neutral Network (CNN)
We will use One dimensional Convolutional Neural Network for text classification. At first, we still add embedding layer then:
- Add Convolutional layer: The Conv1D slide a small window (kernel size) across the input sequences, applying convolutional operations to capture local patterns and features.
- Add Max pooling layer (GlobalMaxPooling1D): The MaxPooling1D layer reduces the dimensionality of output and retain the most relevant features.
- Finally, add a dense layer with 1 neuron and
sigmoidactivation perform the final classification by learning higher-level representations from the extracted features.
#Convolutional Neural Network 1D
cnn_model = Sequential()
embedding_layer = Embedding(vocab_size, 100, weights=[embedding_matrix],input_length=maxlen, trainable=False)
cnn_model.add(embedding_layer)
# adding convolutional layer
cnn_model.add(Conv1D(128, 5, activation='relu')) #128 filters, kernel size 5x5, activation relu
# adding max pooling layer
cnn_model.add(GlobalMaxPool1D())
cnn_model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))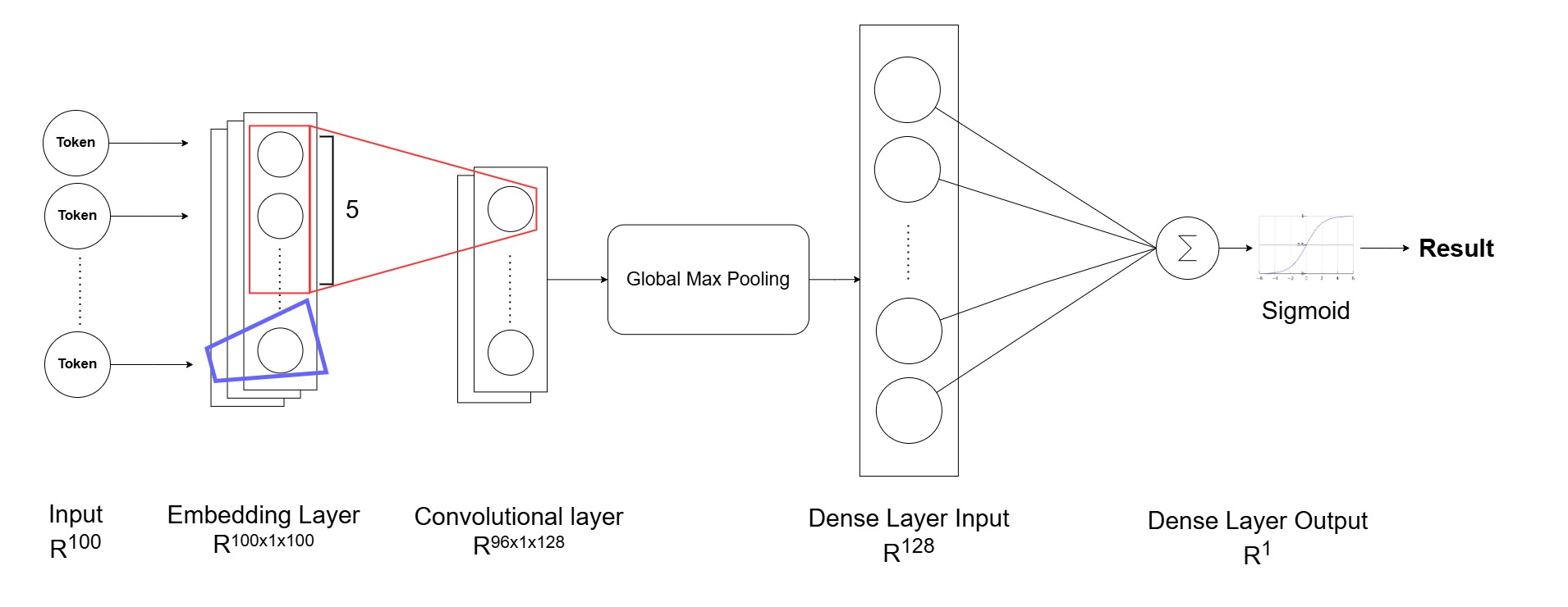
CNN architecture


In the Accuracy tab, it look like better than simple neural network. The curve of both accuracy and loss on testing set fitter with curve of training set. Its mean that this model performs better than simple neural network. But it is still overfitting. Accuracy on test set just around 85% while above 92% in traing set.
Lets move to next model to see whether it better than this.
Long Short-term Memory (LSTM)
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) is a type of neural network designed for sequential data. It’s great for sentiment analysis because it understands word order, captures context, and works with variable-length text. LSTMs automatically learn important patterns for sentiment prediction, making them powerful for natural language processing tasks.
To build our LSTM model, we still do the same but adding LSTM layer after embedding layer
#LSTM
LSTM_model = Sequential()
embedding_layer = Embedding(vocab_size, 100, weights=[embedding_matrix],input_length=maxlen, trainable=False)
LSTM_model.add(embedding_layer)
# adding LSTM layer
LSTM_model.add(LSTM(128)) #don't need to set return_sequences
# adding dense layer
LSTM_model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
LSTM architecture


The model best fit with the data, both loss curve and accuracy curve on testing set really nice, it both bending almost the same with curve of training set. Moreover, accuracy is really high, above 86% and as the result, loss would be very low (under 33%)
Inference
After training, we will use those our model to inference on Amazon review dataset and build a simple Streamlit app with Youtube API from Google Cloud Platform to do sentiment predict with Youtube comment
Predict on Amazon review dataset

Our model work pretty well on this dataset, now we will build a streamlit app to infer our models on youtube comments real-time
Youtube Comments Analyzing
To use app, firstly generate API_KEY via Google Cloud Platform (GCP) in link: https://console.cloud.google.com/ (make sure you enable YouTube Data API v3 already on GCP)
You can find the detail instruction here: https://developers.google.com/youtube/v3/getting-started?hl=en
After running with streamlit run main.py we’ll see some funny tabs
We can select one of our 3 models (MLP, CNN, LSTM) to use for infer the random text

I will try predicting this link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zasSHid4TGU about Black Myth Wukong Celestial Symphony. This inferences will use default LSTM model (the best model) to apply.


Conclusion
The project try comparing 3 model (MLP, CNN 1D, LSTM) on the same task Sentiment Analysis. Can see that the accuracy of MLP < CNN < LSTM when training on IMDB review dataset. Because of a learning project, there are still some aspaect that not good. But still value for learning and understand the basic concept in deep learning and NLP.
-Mew-
References
Pre-trained word embedding using glove in nlp models - GeeksforGeeks
Sentiment Analysis with NLP & Deep Learning - analyticsvidhya
Related
Spotify Analysis
Analyze data from Spotify platform utilizing the Spotify API and MongoDB, Apache Hadoop, Pyspark, Dremio and Power BI
Read more...